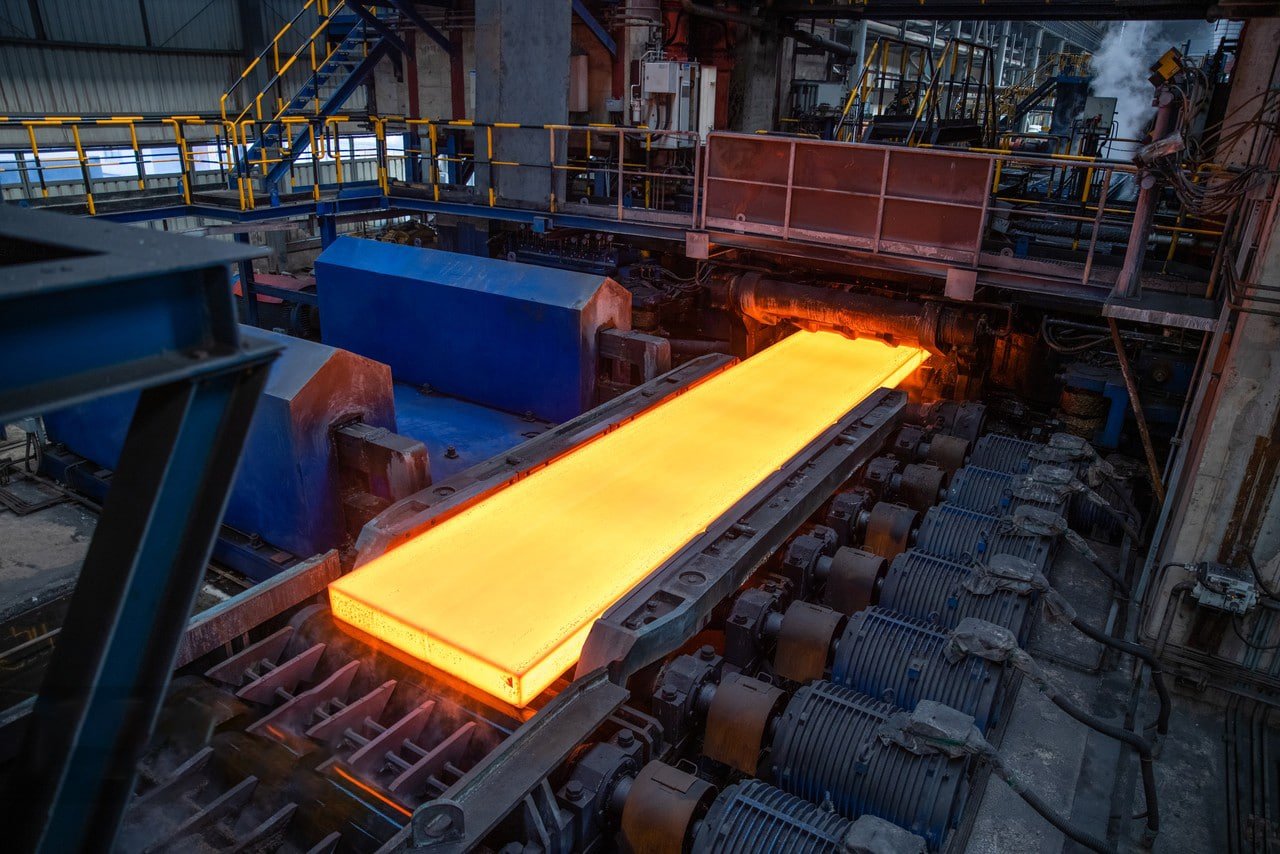
Are you confused about whether to use stainless steel sheets or plates for your project? Understanding their key differences can save you from costly mistakes and ensure optimal performance.
Stainless steel sheets and plates are distinguished primarily by thickness - sheets are typically less than 6mm thick1, while plates are 6mm or thicker. This fundamental difference affects their applications, manufacturing processes, and handling requirements.
The choice between stainless steel sheets and plates can significantly impact your project's success. While both are made from corrosion-resistant steel alloys, their distinct characteristics make them suitable for different applications. Let's explore these differences to help you make an informed decision.
Recent market analysis shows growing demand for both products, with sheets dominating in volume2 due to their versatility in lighter applications, while plates command higher value in heavy industrial sectors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for project planning and cost management.
How Do Thickness and Dimensions Differentiate Stainless Steel Sheets from Plates?
Choosing the wrong thickness can lead to material waste and project delays. Understanding dimensional differences helps ensure proper material specification and optimal performance.
The primary dimensional difference lies in thickness: sheets range from 0.13mm to 6mm3, while plates start at 6mm and can exceed 50mm. This thickness variation affects everything from handling requirements to manufacturing processes.

Dimensional Specifications
| Characteristic | Stainless Steel Sheets | Stainless Steel Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness Range | 0.13mm - 6mm | 6mm - 50mm+ |
| Standard Widths | 600mm - 2000mm | 1000mm - 3000mm |
| Length Options | Up to 6000mm | Up to 12000mm |
Weight and Handling Differences
| Aspect | Sheets | Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Weight per m² | 1-48 kg | 48-400+ kg |
| Handling Equipment | Manual possible | Crane required |
| Transportation | Standard packaging | Special arrangements |
Manufacturing Tolerances
| Parameter | Sheet Tolerance | Plate Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | ±0.1mm - ±0.3mm | ±0.35mm - ±1.0mm |
| Width | ±2mm - ±5mm | ±5mm - ±10mm |
| Flatness | Tighter | More variation |
What Are the Common Applications for Stainless Steel Sheets Versus Plates?
Mismatching material to application can result in performance failures and unnecessary costs. Understanding typical applications helps in making the right choice for your specific needs.
Sheets are commonly used in lightweight applications like appliances, architectural panels, and food equipment4. Plates are preferred for heavy-duty applications such as pressure vessels, structural supports, and industrial equipment.

Application Comparison
| Industry Sector | Sheet Applications | Plate Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Cladding, Roofing | Support structures, Bridges |
| Manufacturing | Equipment housing | Machine bases |
| Chemical | Light tanks, Ducting | Pressure vessels, Reactors |
Load-Bearing Capacity
| Material Type | Load Capacity | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Sheets | Light to medium | Decorative, Light structural |
| Plates | Heavy duty | Load-bearing, Structural |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
| Factor | Sheets | Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost/m² | Lower | Higher |
| Installation Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
How Are Stainless Steel Sheets and Plates Manufactured and Processed Differently?
Understanding manufacturing differences is crucial as they directly impact material properties and costs. Different processing methods result in distinct characteristics suitable for various applications.
Sheets typically undergo cold rolling for precise thickness control and superior surface finish, while plates are primarily hot rolled5. These different processes affect mechanical properties, surface quality, and fabrication options.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
| Process Stage | Sheets | Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Method | Primarily cold rolled | Hot rolled |
| Temperature Control | Room temperature | Above 900°C |
| Surface Finish Options | Multiple (2B, BA, #4) | Limited (Hot rolled, pickled) |
Processing Equipment Requirements
| Equipment Type | Sheet Processing | Plate Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Rolling Mills | Precision cold mills | Heavy-duty hot mills |
| Handling Systems | Light-duty equipment | Heavy cranes |
| Finishing Equipment | Multiple options | Limited options |
Quality Control Parameters
| Parameter | Sheet Standards | Plate Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Very strict | Less stringent |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Tighter | Wider |
| Flatness Requirements | More critical | Less critical |
Which Industries Prefer Stainless Steel Sheets and Which Prefer Plates?
Different industries have specific requirements that make either sheets or plates more suitable. Understanding these preferences helps in market positioning and application selection.
Light manufacturing and consumer goods industries typically prefer sheets, while heavy industry, construction, and marine sectors favor plates. This division is based on load requirements, fabrication needs, and application specifications.

Industry Preference Analysis
| Industry | Preferred Type | Reason for Preference |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Sheets | Weight reduction, formability |
| Oil & Gas | Plates | Strength, pressure resistance |
| Food Processing | Sheets | Hygiene, easy cleaning |
| Shipbuilding | Plates | Structural integrity |
Application-Specific Requirements
| Requirement | Sheet Suitability | Plate Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Forming | Excellent | Limited |
| Welding | Good | Excellent |
| Surface Finish | Superior | Standard |
Cost Considerations by Industry
| Industry Sector | Material Cost Impact | Processing Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Goods | Lower, high volume | Moderate processing |
| Heavy Industry | Higher, lower volume | Extensive processing |
| Construction | Variable | Project-specific |
How to Choose Between Stainless Steel Sheets and Plates for Your Project?
Making the right choice between sheets and plates is crucial for project success. Consider these key factors to ensure optimal material selection.
Selection depends on load requirements, fabrication needs, cost constraints, and application environment. Consider thickness requirements, forming needs, and installation methods when making your choice.

Decision Matrix
| Factor | Choose Sheets If | Choose Plates If |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness Needed | <6mm | >6mm |
| Load Bearing | Light to medium | Heavy duty |
| Forming Requirements | Complex forming needed | Minimal forming needed |
Cost Comparison Factors
| Cost Element | Sheets | Plates |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost/kg | Higher | Lower |
| Processing Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Installation Cost | Lower | Higher |
Application Success Factors
| Success Factor | Sheet Performance | Plate Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Optimization | Better | Limited |
| Structural Integrity | Good for light loads | Excellent for heavy loads |
| Maintenance | Generally easier | More demanding |
Conclusion
The choice between stainless steel sheets and plates depends on specific application requirements, with sheets excelling in light applications and plates in heavy-duty scenarios.
-
Learn about standard thickness ranges for sheets and plates ↩
-
Understand market demand dynamics for sheets vs plates ↩
-
Discover specific thickness ranges for stainless steel sheets ↩
-
Explore typical uses of stainless steel sheets across industries ↩
-
Understand the manufacturing process differences between cold and hot rolled steel ↩






